Installation
Getting Started with Parlant
Parlant is an open-source Alignment Engine for conversational LLM agents, built to help developers quickly create engaging and compliant customer-facing agents with control, clarity, and confidence.
It gives you all the structure you need to build AI agents that behave exactly as your business requires:
-
Journeys: Define clear customer journeys and how your agent should respond at each step.
-
Behavioral Guidelines: Easily craft agent behavior; Parlant will match the relevant elements contextually.
-
Tool Use: Attach external APIs, data fetchers, or backend services to specific interaction events.
-
Domain Adaptation: Teach your agent domain-specific terminology and craft personalized responses.
-
Canned Responses: Use response templates to eliminate hallucinations and guarantee style consistency.
-
Explainability: Understand why and when each guideline was matched and followed.
How It Works
When your agent receives a message, Parlant's engine prepares a fully-aligned response before generating it:
The guidelines and tools relevant to the current conversational state are carefully matched and enforced, keeping your agent focused and aligned, even with complex behavioral configurations.
Installation
Parlant is available on both GitHub and PyPI and works on multiple platforms (Windows, Mac, and Linux).
Please note that Python 3.10 and up is required for Parlant to run properly.
pip install parlant
If you're feeling adventurous and want to try out new features, you can install the latest development version from GitHub.
pip install git+https://github.com/emcie-co/parlant@develop
Creating Your First Agent
Once installed, you can use the following code to spin up an initial agent. You'll flesh out its behavior later.
# main.py
import asyncio
import parlant.sdk as p
async def main():
async with p.Server() as server:
agent = await server.create_agent(
name="Otto Carmen",
description="You work at a car dealership",
)
asyncio.run(main())
What's with the async/await?
You'll notice Parlant follows the asynchronous programming paradigm with async and await. This is a powerful feature of modern Python that lets you to write code that can handle many tasks at once, allowing your agent to handle more concurrent requests in production with less compute resources.
If you're new to async programming, check out the official Python documentation for a quick introduction.
NLP Service Configuration
Parlant uses Emcie as the default NLP service, since Emcie's models were specifically optimized for Parlant's engine (guideline matching, message generation, etc.), resulting in lower costs and reduced latency compared to general-purpose model providers. To use Emcie, set your API key and run the program:
export EMCIE_API_KEY="<YOUR_API_KEY>"
Now run the program:
python main.py
Parlant supports multiple LLM providers via the p.NLPServices class.
To use an alternative provider, specify it when creating the server:
async with p.Server(nlp_service=p.NLPServices.openai) as server:
...
Supported providers
| Provider | Extra Package | Environment Variable |
|---|---|---|
| Emcie (default) | Built-in | EMCIE_API_KEY |
| OpenAI | Built-in | OPENAI_API_KEY |
| Anthropic | parlant[anthropic] | ANTHROPIC_API_KEY |
| Google Gemini | parlant[gemini] | GOOGLE_API_KEY |
| Google Vertex AI | parlant[vertex] | Google Cloud credentials |
| AWS Bedrock | parlant[aws] | AWS credentials |
| Azure OpenAI | parlant[azure] | AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY |
| Cerebras | parlant[cerebras] | CEREBRAS_API_KEY |
| Together AI | parlant[together] | TOGETHER_API_KEY |
| DeepSeek | parlant[deepseek] | DEEPSEEK_API_KEY |
| Ollama | parlant[ollama] | — (local) |
| LiteLLM | parlant[litellm] | Varies by underlying provider |
For the full, up-to-date list of supported providers, see pyproject.toml and the p.NLPServices factory class.
For providers that require an extra package, make sure to install it with pip:
pip install "parlant[anthropic]"
You can also implement your own provider via the p.NLPService interface—see Custom NLP Models for details.
Testing Your Agent
To test your installation, head over to http://localhost:8800 and start a new session with the agent.
Creating Your First Guideline
Guidelines are the core of Parlant's alignment model. They allow you to define how your agent should respond to specific user inputs or conditions. Parlant cleverly manages guideline context for you, so you can add as many guidelines as you need without worrying about context overload or other scale issues.
# main.py
import asyncio
import parlant.sdk as p
async def main():
async with p.Server() as server:
agent = await server.create_agent(
name="Otto Carmen",
description="You work at a car dealership",
)
##############################
## Add the following: ##
##############################
await agent.create_guideline(
# This is when the guideline will be triggered
condition="the customer greets you",
# This is what the guideline instructs the agent to do
action="offer a refreshing drink",
)
asyncio.run(main())
Now re-run the program:
python main.py
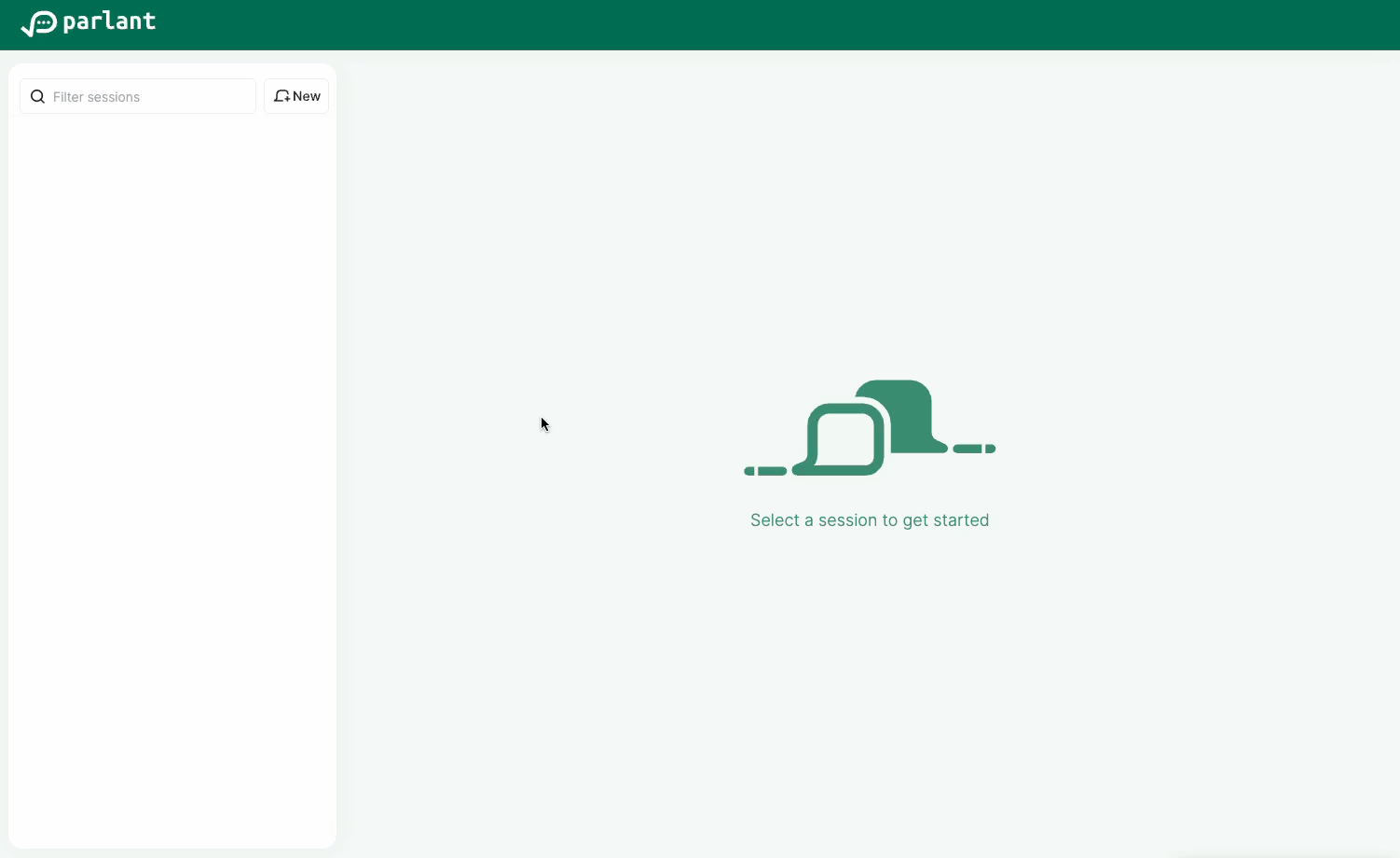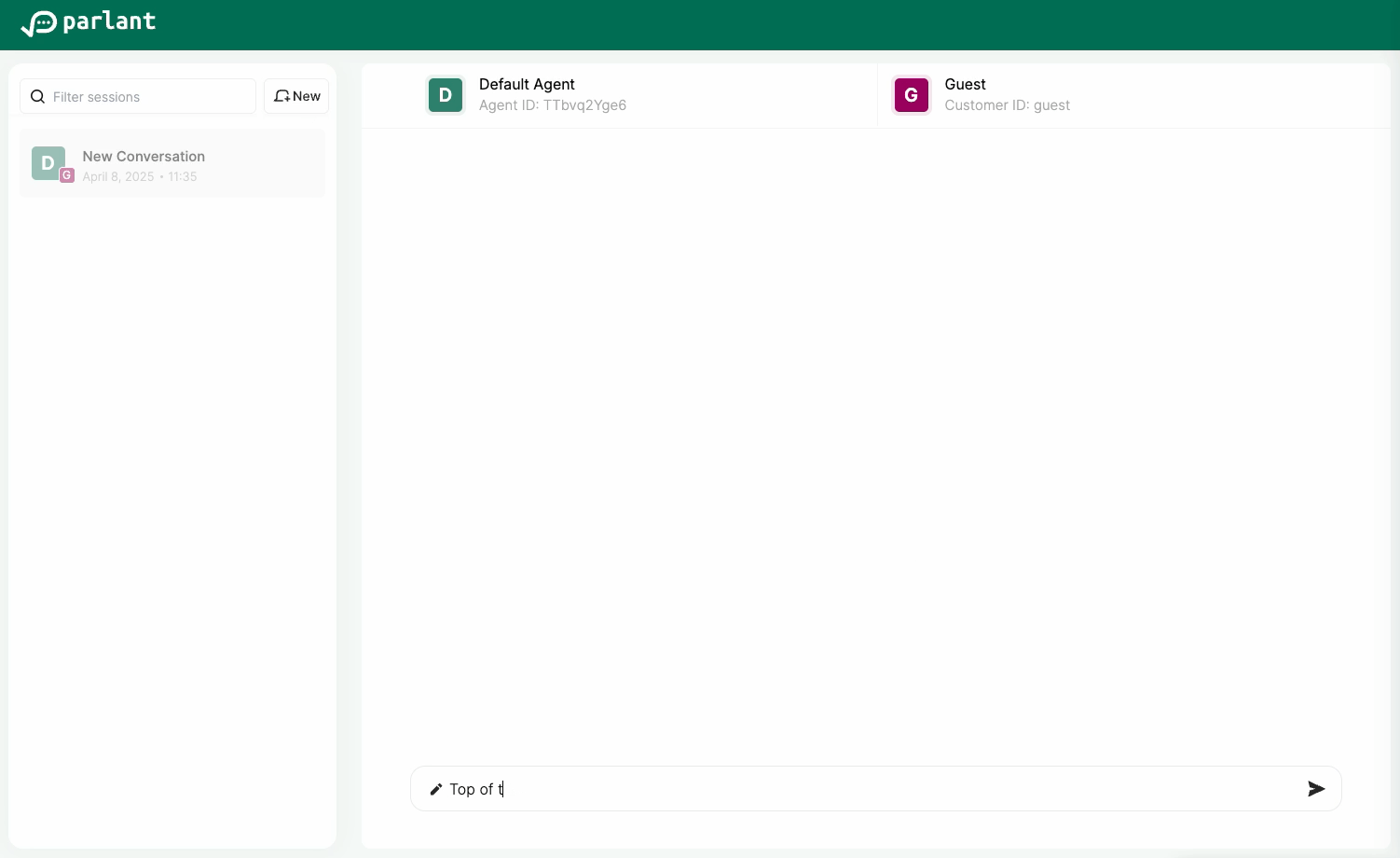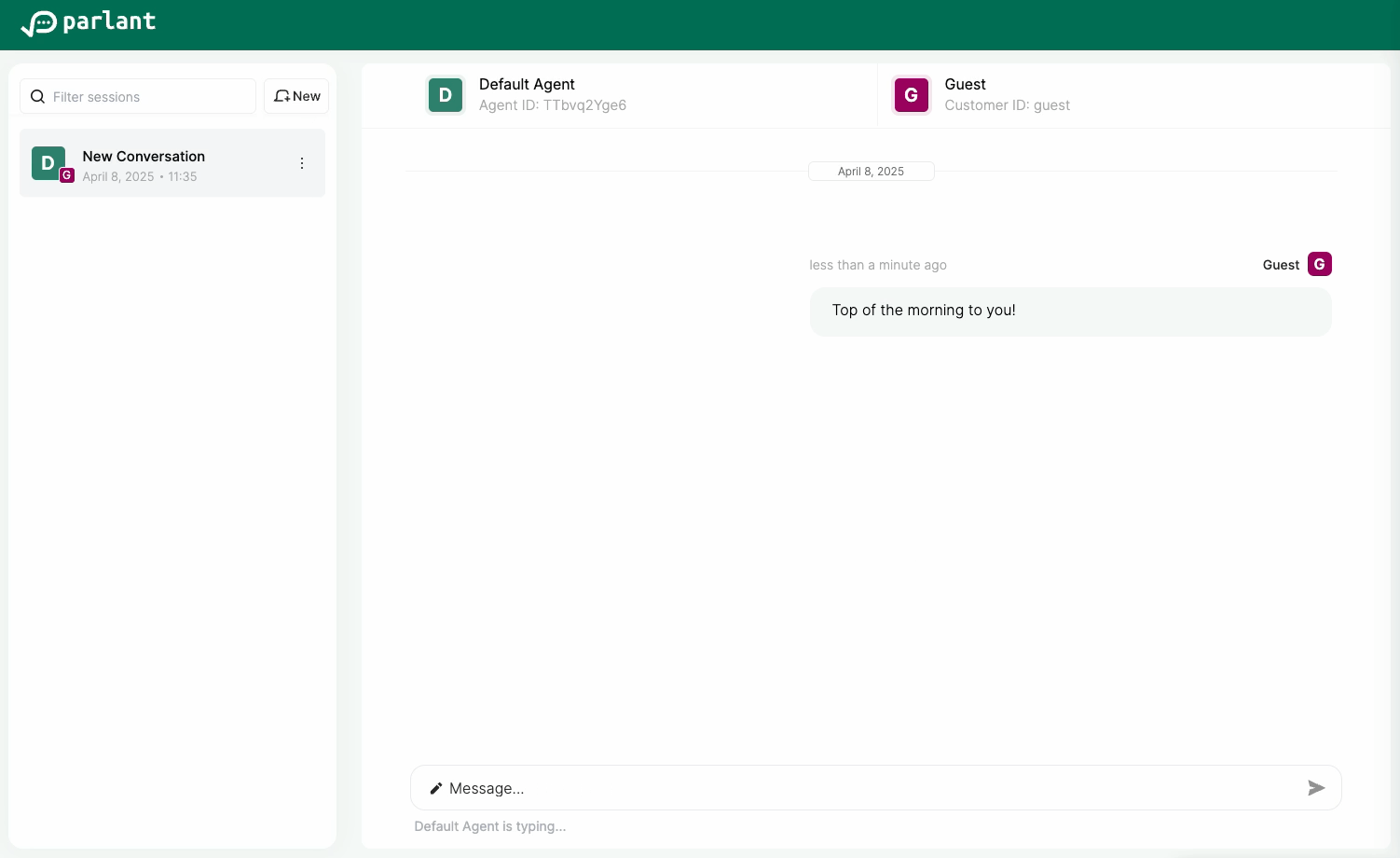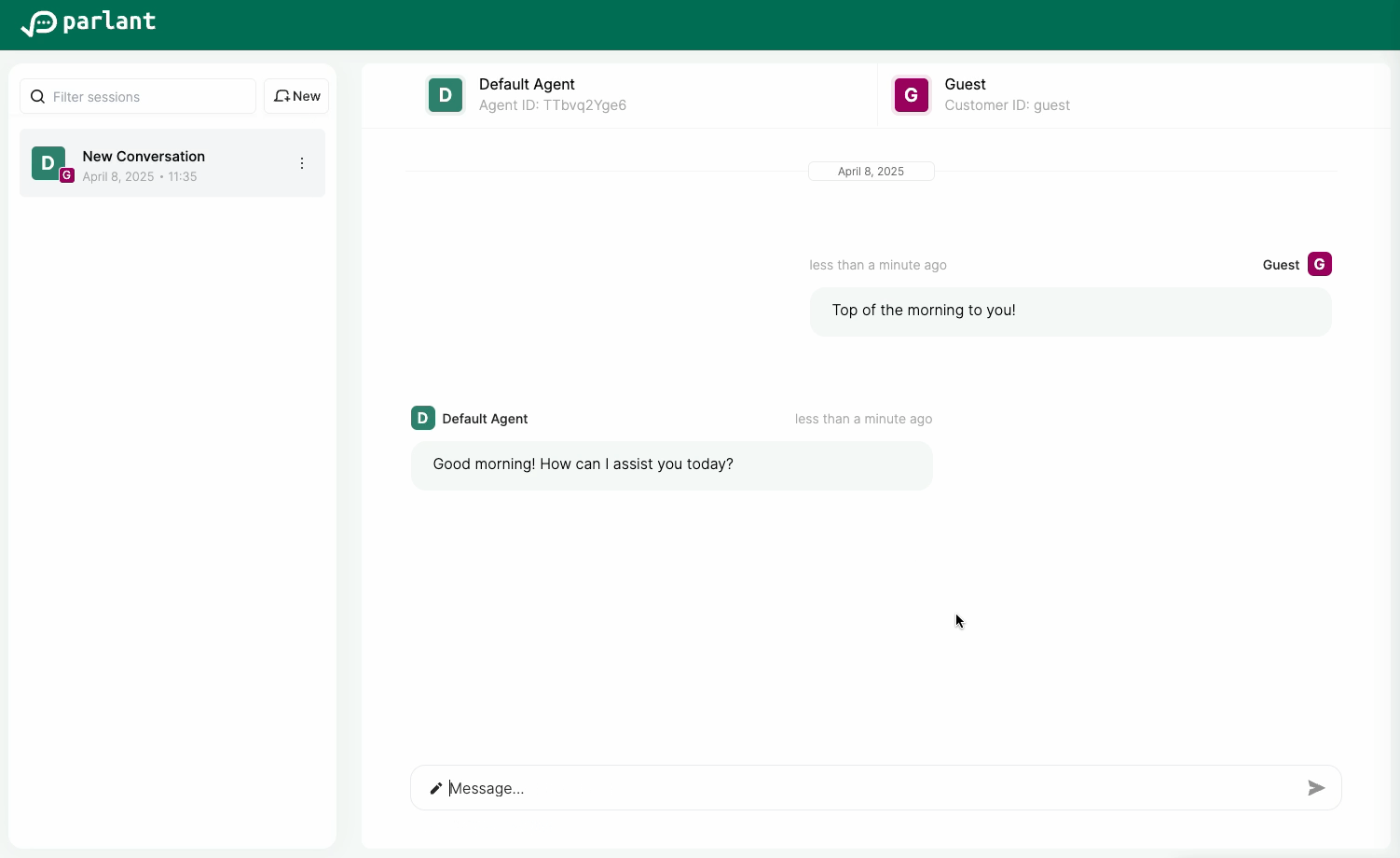
Refresh http://localhost:8800, start a new session, and greet the agent. You should expect to be offered a drink!
Using the Official React Widget
If your frontend project is built with React, the fastest and easiest way to start is to use the official Parlant React widget to integrate with the server.
Here's a basic code example to get started:
import React from 'react';
import ParlantChatbox from 'parlant-chat-react';
function App() {
return (
<div>
<h1>My Application</h1>
<ParlantChatbox server="PARLANT_SERVER_URL" agentId="AGENT_ID" />
</div>
);
}
export default App;
For more documentation and customization, see the GitHub repo: https://github.com/emcie-co/parlant-chat-react.
npm install parlant-chat-react
Installing Client SDK(s)
To create a custom frontend app that interacts with the Parlant server, we recommend installing our native client SDKs. We currently support Python and TypeScript (also works with JavaScript).
Python
pip install parlant-client
TypeScript/JavaScript
npm install "github:emcie-co/parlant-client-typescript#v3.1.2"
You can review our tutorial on integrating a custom frontend here: Custom Frontend Integration.
For other languages—they are coming soon! Meanwhile you can use the REST API directly.